A freight carrier’s airway bill (AWB) is a document that confirms receipt of a shipment for air carriage. So, what is the function of the airway bill, what is the exact content, and how do you check it up? Learn more about Best Logistics in this article!
Functions of Airway bill (AWB)
The air waybill (airway bill) serves two major purposes:
– As a receipt for the carrier’s delivery;
– As proof of transportation contract.
It should be noted that the Airway bill is not a transferable title document like a bill of lading (of order type), but rather a document for the air carriage of goods. If you want to pay by letter of credit (L/C) in extraordinary circumstances, the two parties must agree and carry out additional steps such as drafting a guarantee commitment and asking the bank to accept the “signature”. return” to the back of the AWB to be able to pick up the items.
Many copies of the original Airway bill bill of lading will be given to various parties such as the carrier, the consignee, the consignee, and so on. Following the arrival of the goods, the consignee or potentially an air freight service agent will go to the carrier’s office to obtain the air waybill and the set of documentation delivered with the products. Depending on the terms of the sales contract, the consignee may also get the Airway bill and the original paperwork via express prior to the arrival of the goods in order to complete the import procedures.
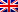
The following information is printed on the front of the Airway bill form:
- AWB number
- Airport of departure
- Issuing carrier’s name and address
- Shipper
- Consignee
- Routine
- Accounting information
- Charges codes
- Currency
- Charges
- Declare value for carriage
- Declare value for customs
- Amount of Insurance
- Handling information
- Number of pieces
- Other charges
- Prepaid
- Collect
- Shipper of certification box
- Carrier of execution box
- For carrier of use only at the destination
- Collect charges in destination currency, for the carrier of use only

Categorization of an Airway bill
- Master Airway Bill (MAWB): This document is sent by the airline to the consolidator together with a bill of lading so that the cargo can be received at the port of entry. The connection between the air carrier and the consolidator is governed by this delivery document between the carrier and the consolidator.
- House Airway Bill (HAWB): This document is produced by the forwarder to modify the contractual arrangement between the consignor and the retail owners and is used to transfer goods between the consolidator and the retail owners. a document given to shippers when they get products from them, when they send goods at the port of export, and when they receive goods at the port of entry.
AWB owns a number of copies and originals.
There will be at least 9 AWB copies total, with 3 copies of the original and at least 6 copies of the copy.
Original #1: The carrier will only be allowed to use this green version. The copy’s main use is to demonstrate the carriage contract. As accounting vouchers, the copies will be preserved. The consignor will sign this copy.
Original version number 2: According to the consignee, this edition is pink. This copy will be sent to the consignee along with the rest of the package to the specified location.
The third original is blue. This duplicate, which belongs to the shipper, was utilized by the carrier as evidence of receipt. Additionally, it will serve as proof of the carriage contract. Both the shipper and the carrier must properly sign this copy.
Best Cargo has provided some of the essential information on benefits and drawbacks of the air transportation. This essay should help you better grasp the modern air transportation industry!
Don’t forget to check out our popular article:
Cargo delivery from Vietnam to Ohio (America)
Aircraft manufacturer – 5 main companies in the industry